Research Page
Biosphere Climate Impacts & Feedbacks
Land-atmosphere fluxes of energy, water, and carbon exert a strong control on atmospheric properties, and thus provide a key forcing for global climate. GSFC has a long history of incorporating remotely sensed data on land properties into land-atmosphere models, including the pioneering Simple Biosphere (SiB) model. This work extends to understanding how human land use, including urbanization, affects regional and global climate.
GSFC researchers are also examining long-term impacts of a changing climate on ecosystem composition, extent, and structure. For example, analysis of long-term records from AVHRR, MODIS and Landsat has revealed systematic increases in high-latitude plant area, and changes in Siberian forest composition.
Areas of Investigation
Circum-Arctic Greening from AVHRR (C. Tucker)
Surface Water Changes in ABoVE Study Domain (M. Carrol)
Siberian Forest Dynamics (J. Ranson)
Urbanization and Climate Impacts (L. Bounoua)
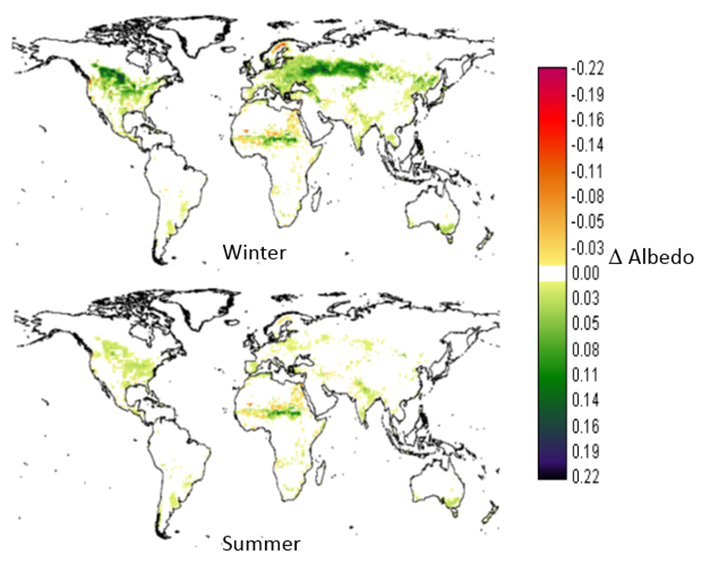
Albedo Consequences of Disturbance and Land Use (J. Masek)
GSFC researchers are also examining long-term impacts of a changing climate on ecosystem composition, extent, and structure. For example, analysis of long-term records from AVHRR, MODIS and Landsat has revealed systematic increases in high-latitude plant area, and changes in Siberian forest composition.
Areas of Investigation
Circum-Arctic Greening from AVHRR (C. Tucker)
Surface Water Changes in ABoVE Study Domain (M. Carrol)
Siberian Forest Dynamics (J. Ranson)
Urbanization and Climate Impacts (L. Bounoua)
Albedo Consequences of Disturbance and Land Use (J. Masek)