Innovation Lab Use Case
Optimize Choice in Neural Network
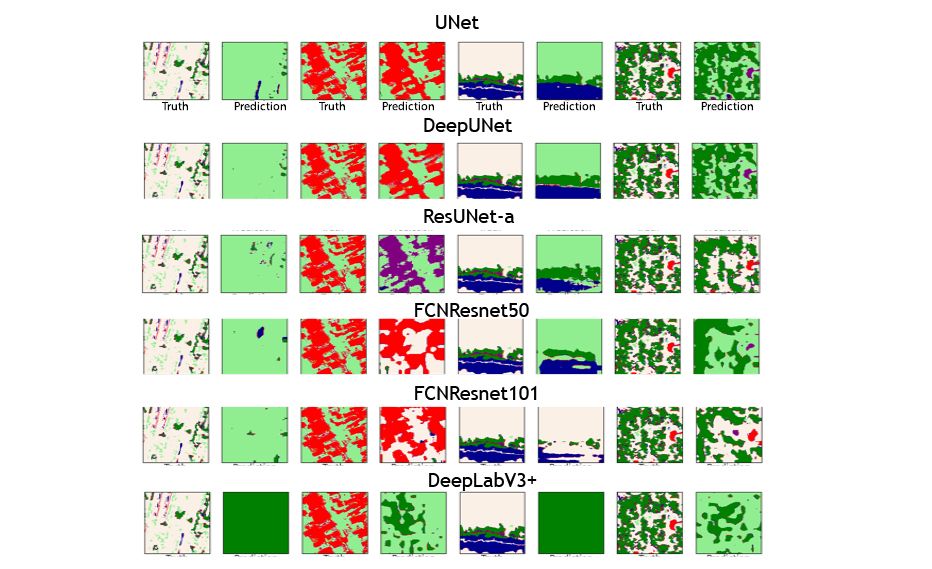
Several state-of-the-art convolutional neural networks were modified for the segmentation of very high-resolution satellite imagery. The applicability of these networks and the effects of underlying hyperparameters was evaluated in the classification of features in 0.5-meter resolution data. The findings were that:
- Some of the most common networks (shown below) are not designed to identify small and sparse objects.
- Training and inference time increases drastically as the network integrates more blocks.
- For Residual Neural Network (ResNet), the bigger the network, the more accurate it becomes.
- Atrous convolutions, as they are, were found to be inefficient at detecting individual pixels that were outside of a small class group.
| Suitability | Performance |
| Small objects accuracy | Memory Requirements |
| Sparse objects accuracy | Training Time |
| Boundary pixels accuracy | Classification Time |
| Overall accuracy | Convergence Speed |
